1. NETWORKING
Networking is the interconnection of two or more computer for the purpose of communicating, sharing information, and other hardware resources. Networking is also known as a Computer network. Computer Network enables devices and endpoints to be connected to each other on a Local Area Network.
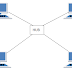
NETWORKING BLOCK DIAGRAM
Advantages:-
a. To share data, information, and programs.
b. To share hardware like printer, scanner, etc.
c. Data backup and recovery.
d. Easy access to files from any computer.
Disadvantages:-
a. Computer virus spreads mostly through the Network.
b. Skill manpower is required to operate Computer Network.
c. It is expensive to set up.
2.
TYPES OF NETWORK
The network can be classified on the basis of Network Architecture and Geographical Coverage.
a.
Network Architecture
On the basis of Network Architecture, the computer networks are classified in two:-
i.
Peer-To-Peer Architecture
In this Architecture, there is no server that manages and controls other computers in the Network. It is also known as Workgroup Architecture. Each computer functions as both a client and a server. There is no dedicated server.
Peer-To-Peer Block Diagram
ii. Client-Server Architecture
In this Architecture, there is at least one server computer and one or more workstations. It is also known as Domain Architecture. All the workstations are connected to the server and communication is done through it. The server always provides services to clients and the client always receives services from the server.
CLIENT-SERVER BLOCK DIAGRAM
b.
Geographical Area Coverage
On the basis of Geographical Area Coverage, the computer networks are classified into three types. They are:-
i. Local Area Network(LAN)
LAN is the interconnection of computers in a limited area like in a single room, rooms within a building, or buildings on one site. It is smaller, simpler and cheaper than other Networks. Most local area networks are built with relatively cheap hardware such as Ethernet cables, network adapters, and hubs.
ii.
Metropolitan Area Network(MAN)
MAN is the network that extends up to a city or a larger geographical area than LAN. A MAN can connect several LANs. It can use wired or wireless transmission media. This network mostly uses bridges, repeaters, routers, switches etc. Example:- Cable TV Network.
iii.
Wide Area Network(WAN)
WAN is the network that is extended to a large area throughout the world or even more. It is also known as Long Haul Networks (LHNs). It is the combination of many types of LAN and MAN Networks. The Internet is an example of WAN.
3.
LAN TOPOLOGIES
The physical or logical layout of cabling for connecting computers on the network is known as LAN Topologies. It is also known as Network Topology. Generally, it is the cabling system in the network.
Types of Network Topologies
a.
Bus Topology
In this topology, all computers are connected directly to the common cable with the help of T-connectors. It is also known as Linear Topology. It consists of the main cable with terminators at both ends.
BUS TOPOLOGY BLOCK DIAGRAM
Advantages:-
i. It is simple, reliable, and easy to use.
ii. It is the cheapest topology to implement.
iii. The failure of one computer doesn’t affect others.
Disadvantages:-
i. If the network bus has a problem, then the entire network fails.
ii. It is difficult to troubleshoot.
iii. It has limited cable length and number of nodes.
b.
Ring Topology
In this topology, all the computers are arranged in the shape of a circle. It is also known as loop topology. In this topology, data is transmitted in only one direction (Either clockwise or Anti-clockwise at a time).
RING TOPOLOGY BLOCK DIAGRAM
Advantages:-
i. It is easy to set up.
ii. It supports a high data transmission rate.
iii. Data traffic is reduced as data flows in only one direction.
Disadvantages:-
i. More expensive than bus topology because of the cost of the MAU (Media Access Unit).
ii. Failure of a computer affects the entire network.
iii. Difficulty in adding and removing the computers from the ring.
c.
Star Topology
Star topology is the most popular topology used to connect computers and other network devices on the network. In a star topology, all nodes are connected through a central device in the form of a star by cable. Data on the star topology passes through the central device before reaching its destination.
STAR TOPOLOGY BLOCK DIAGRAM
Advantages:-
i. It is easier to add or remove computers.
ii. The failure of one computer doesn’t affect the entire network.
iii. Easy to troubleshoot the failure.
Disadvantages:-
i. The entire network fails if there is any problem on the central devices.
ii. It is expensive than bus topology
iii. Data traffic, data collision rate, and data The error rate will be high.
d.
Tree Topology
In computer networks, tree topology is also known as a star bus topology. It contains elements of both a bus topology and a star topology.
TREE TOPOLOGY BLOCK DIAGRAM
Advantages:-
i. It is easy to extend.
ii. Easy to troubleshoot compare to bus topology.
iii. Easy to connecting and removing devices.
Disadvantages:-
i. The failure of the main root affects the entire network.
ii. It is complex to configure.
iii. It requires more cables and central devices.
e.
Mesh Topology
In this topology, each computer is connected to all other computers of the forming a mesh. It requires more cable for each and every connection.
MESH TOPOLOGY BLOCK DIAGRAM
Advantages:-
i. Failure of a device does not affect the data transmission to the destination device.
ii. Data transmission is faster.
iii. Less data collision and data error rate.
Disadvantages:-
i. It is very complex.
ii. More cables are required
iii. It is difficult to manage.
f.
Hybrid Topology
Hybrid Topology is a combination of two or more topology. Networks are widely designed by using this
topology. Some of the commonly used hybrid topologies are a Star-Bus topology,
Star-Ring topology, Bus-Ring topology.
4.
Transmission Media
Transmission media refers to the wires, cables, and other
means through which data travels from its source to destination.
There are two types of transmission media. They are:-
a.
Guided/Bounded/ Wired Media
The transmission media which use cables are called guided or
bounded or wired media. There are three types of cables used in the wired
network:-
i.
Twisted pair cable
Twisted pair cable is the oldest and still most common
transmission media. It contains a pair of cables, twisted each other. It is
cheaper, lighter, thinner, more flexible, and easier to install. A twisted pair
cable is connected with the help of an RJ-45 connector. Unshielded and shielded
twisted pair cables are the types of twisted pair cable. Unshielded Twisted Pair
cable does not contain extra covering but Shielded Twisted Pair Cable contains
an extra metal covering.
ii.
Coaxial Cable (Coax)
The coaxial cable carries data signals for higher frequency and at
a faster speed than twisted pair cable. It is common to use for the transmission
of signals in cable television systems and broadband transmission. Coaxial Cable
has a large bandwidth, which can handle plenty of traffic at high speeds. The
BNC (Bayonet-Neil-Concelman) connector is used to connecting this cable.
iii.
Fiber-Optics Cable(Optical Fiber Cable)
Fiber-Optics Cable is made of glass or plastic and transmits
signals in the form of light. It contains single or multiple hairs of glass
fibers wrapped by a protective jacket. Fiber-Optic cable can carry voice,
video, and data. It has very high bandwidth and can carry signals for extremely
long distances. S-T connector is used to connect this cable.
b.
Unguided/Unbounded/Wireless Media
The transmission media without cables are called unguided or
unbounded or wireless media. In this media data or signals flow through the
air. They do not flow through the wire or cables. There are three medium used
in wireless media:-
i.
Microwave System
The microwave system uses very high-frequency radio signals to
transmit data through the air. The transmitter and receiver of a microwave
system should be in life-of-sight because the radio signal cannot bend. With
microwave, the very long-distance transmission is not possible. In order to overcome
the problem of the line of sight and shorter distance, repeaters are used at
intervals of 25 to 30 kilometers apart.
ii.
Satellite Communication
Satellite
communication is the most common worldwide communication system at present. It
uses a satellite as a repeater. The satellite is the repeater that orbits in
space. Satellite communication systems have receivers and transmitters located
in ground stations. In this communication, the microwave signal is transmitted
from a transmitter on earth to the satellite in space. The satellite amplifies
the weak signal and transmits it back to the receiver. To make communication
possible in the even longer distance, multiple satellites are used.
iii.
Infrared Technology
Infrared
signals can be used for short-range communication in a closed area using
line-of-sight communication. As infrared signals have a high frequency, it cannot
penetrate the wall. It is mainly used in wireless remote control, wireless LAN (WLAN),
wireless mouse, and keyboard. It cannot be used outside the building because
sun rays contain infrared waves that can interface with communication.
5.
Network Connecting Devices
a.
NIC
NIC stands
for Network Interface Card. It is the device that connects computers and network
cable. The cards are installed in an expansion slot on each computer or built
into the system. NIC has a unique MAC or Physical address, which is stored in
ROM. It helps to control the flow of data between the computer and the cabling
system.
b.
HUB
HUB is a device with multiple ports for connecting different computers on the network. It
accepts data, amplifies them, and then broadcasts. It cannot filter network
traffic and it can connect limited computers only.
c.
Switch
Switch is
a computer networking device that connects computers and other network devices.
it is also known as an intelligent hub. When the switch receives data, it
creates a direct connection between sender and receiver and forwards the data
packet to the destination computer only.
d.
Router
A router
is a device that connects multiple networks having the same protocol. Its main job
is to find out the best path that can be used for data transmission. Routers
are responsible for getting traffic from here to there.
e.
Repeater
Repeater
is a network device that accepts weak signals and regenerates or amplifies
them. It is used to increase the length of the transmission media, in which
data can be transmitted. It receives signals, amplifies them, and retransmits
towards the receiver.
f.
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi
refers to Wireless Fidelity. It enables devices such as laptops, mobile phones,
smart-phone, etc can connect to the network or internet when within range of a
wireless network connected to the internet.
6.
Some Basic Terms Used in Computer
Network
a.
IP Addresses
IP Addresses (Internet
Protocol Address) is a unique identifying number assigned to each computing
devices connected in a network that uses the Internet Protocol for
communication. Example:-216.27.61.137. An
IP addresses have two main functions: identification of network and identification
of a particular host (computer). IPv4 has a 32-bit number and IPv6 has 128-bits
number. IPv4 uses the decimal number and IPv6 uses a hexadecimal number system.
b.
MAC Addresses
MAC
(Media Control Access) is a unique number associated with a network adapter. It
also known as physical or hardware addresses. It is used to uniquely identify
each computer. MAC address is usually assigned by the manufacturer of a network
interface card and is stored in its ROM.
c.
Internet
Internet is
the largest computer network system in the world. It is a global network of
computer networks. Millions of computers around the world can share information
at the same time by using this worldwide network system.
d.
Intranet
An an intranet is a private network that can only be accessed by authorized users. It is under the
control of a single administrative entity. The internet is the internal network
of an organization.
e.
Extranet
An extranet is a private intranet that can be accessed by outside users over the
internet using the dedicated and secure channel. To gain entrance to the
extranet's resource, an external user typically must log on to the networks by
providing a valid user ID and Password.
f.
WWW
WWW
refers to the World Wide Web. It is also commonly known as 'The Web'. WWW consists
of pages that can be accessed using a Web browser. It helps to serve the
webpage to the internet user.
g.
VPN
VPN
stands for Virtual Private Network. A virtual private network (VPN) gives you online privacy and anonymity by creating a private
network from a public internet connection. VPN services establish secure and
encrypted connections to provide greater privacy












No comments